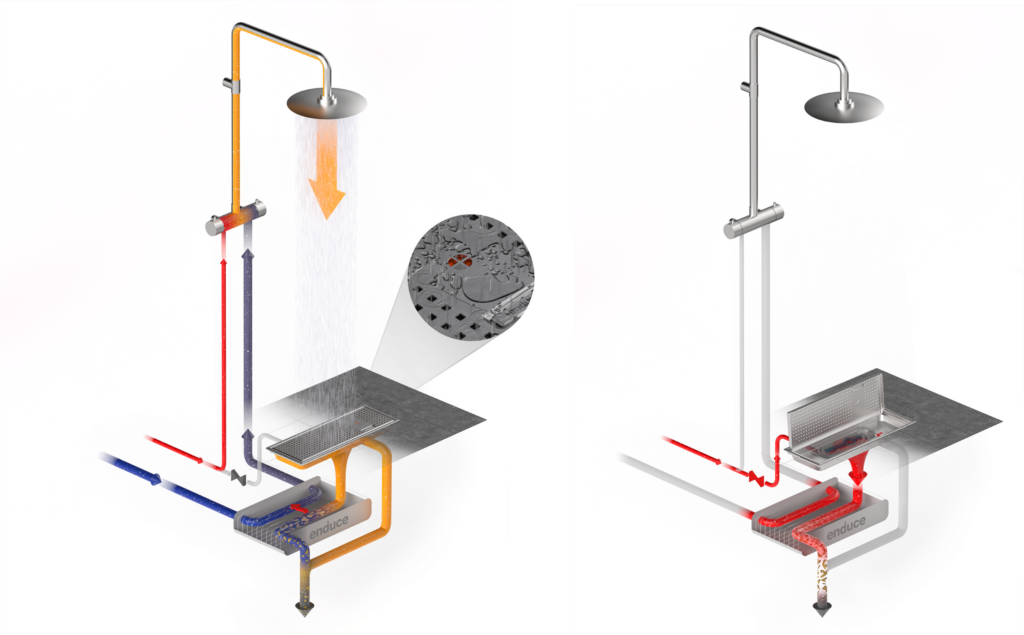
Enduce does not reduce water consumption overall, but hot water consumption is reduced.
Energy is by far the largest resource use in showering - not water. That is, the resource consumption is mainly related to the heating of water rather than water consumption.
We have examined the resource consumption of showering from a system perspective from water source to treatment plant, based on available research. The analysis shows that over 96% of the resource consumption is spent on heating the shower water, while water consumption is only about 4%.
If the analysis is done for all domestic hot water, including cold tap water, the corresponding figure is 90%. If the water source is seawater (3.5 % by weight NaCl) instead of freshwater, an additional 4 percentage points of resource consumption for desalination is added - and the resource consumption for water production and purification for showering has increased to a total of about 8 % of the total resource consumption for showering (heating in this case is still over 90 %).
Source: Erika Wallén, Life cycle assessment of drinking water - a study of a waterworks in Gothenburg, 1999.